Carbohydrates: Nutrition 101 [INFOGRAPHIC]
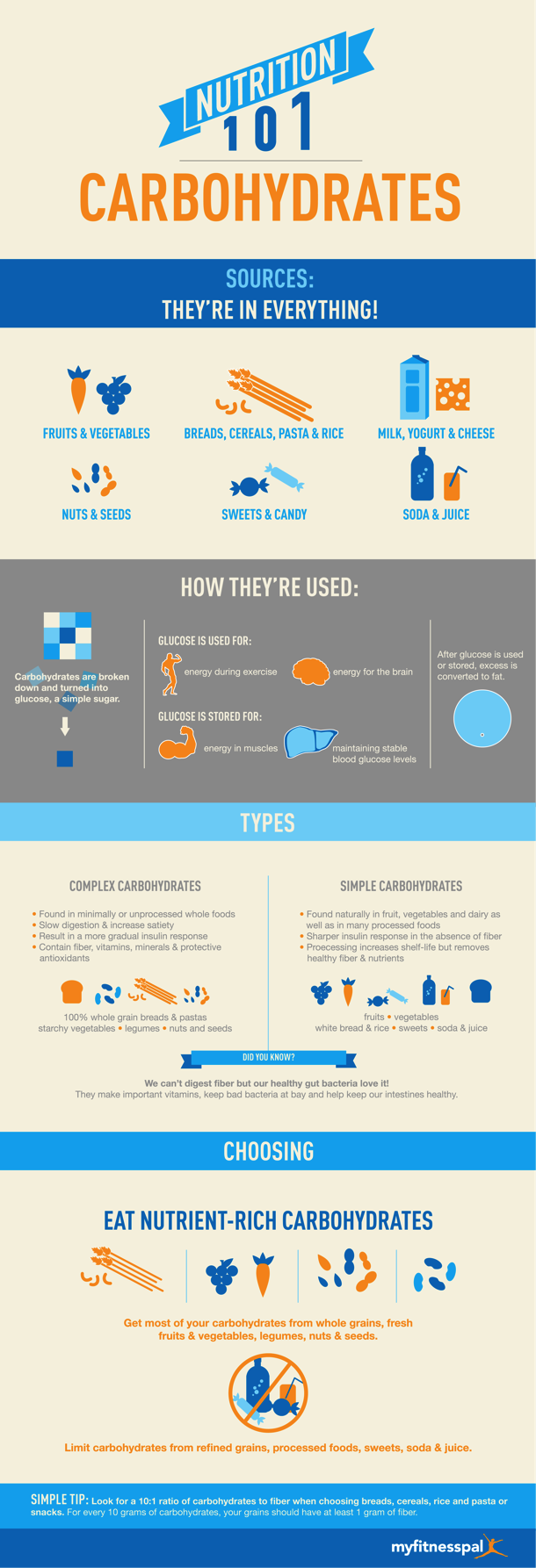
Continuing with our Nutrition 101 series, today we’re talking carbohydrates! Love ‘em or leave ‘em (personally, I’m a fan), carbohydrates are found in pretty much everything – fruits and vegetables, grains, nuts and seeds, dairy, sweets, soda, the list goes on. It’s a good thing too because carbohydrates provide around half of the energy in a well balanced diet, 45-65% of calories according to the most recent Dietary Guidelines for Americans, and similarly so in Australia and the UK.
First, lets talk carbohydrate metabolism, how our body breaks them down and uses them.
After eating a meal, carbohydrates are separated from dietary fiber and broken down into three monosaccharides: glucose, fructose and galactose. These monosaccharides are absorbed in the small intestine and enter the the blood stream. Much like a car that runs on unleaded fuel, our cells only take up carbohydrates in the form of glucose, so the liver then converts all of the fructose and galactose into glucose.
Glucose is transported through the blood stream and is:
- Immediately taken up by cells and turned into energy
- Stored as glycogen by the liver and skeletal muscles (Glycogen in muscles is turned back into glucose for energy during exercise and liver glycogen is what maintains our blood glucose levels during short fasting periods, like while we sleep.)
- Converted into fatty acids and triglycerides for long-term energy storage, if consumed in excess
They may all be broken down and turned into glucose, but all carbohydrates are not created equal. Some are more nutritionally dense than others; different types are digested at different rates and have different impacts on our blood sugar. So lets compare the two main types, complex and simple carbohydrates:
Complex carbohydrates are largely found in whole grains, starchy vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds. What makes them complex, you ask? They contain longer, more complex chains of sugars and generally also contain some fiber, protein and/or healthy fats, as well as important vitamins and minerals. The presence of fiber, protein and fats slows digestion and therefore absorption of those monosaccharides, resulting in a more gradual insulin response as well as increased satiety–both very good things.
Simple carbohydrates come from healthy foods like fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy, but also less nutritionally-dense foods like refined grains (white bread, white rice and traditional pasta), processed snacks and crackers, sweets and sugar-sweetened beverages like sodas. What makes them simple? These foods contain mostly mono- and disaccharides, one and two-molecule sugars that are very quickly digested and absorbed into the bloodstream -quite the opposite of complex carbs. This isn’t necessarily all bad though. Fruits, vegetables and dairy offer good stuff like vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and phytochemicals, fiber and water, which is why they’re so good for you. Refined grains, sweets and sodas on the other hand, are lacking all of these extra nutrients, which is why we should limit these foods in our diet.
When it comes to choosing carbohydrates to eat or drink, nutrient-dense sources are definitely the way to go. These include complex carbs like 100% whole grain breads and pasta, brown rice, starchy vegetables (just leave the nutrient-rich skins on those potatoes), legumes, nuts, seeds, low-fat dairy and plenty of fruits and vegetables. We want to maximize nutrition density and satiety from carbohydrates, so limiting simple sugars from refined grains, processed snack foods, sweets, and sugar-sweetened beverages is best.
Carbs have undoubtedly gotten a bad wrap (couldn’t resist the misspelling) over recent years but whether you love them or not–they’re in everything–and we can certainly all benefit from choosing the more nutrient-dense kinds.